The Amazon River in South America is the largest in the world based on its discharge volume of water. The Amazon River map shows its major tributaries and watershed areas. The origin of the Amazon River is the Montaro River on the Cordillera Rumi Cruz in Peru. After joining with some other tributaries, it forms the Ucayali River, which is considered the main stem of the Amazon River.
The Amazon River enters Brazil from Peru, which has one-fifth part of the total flow of water discharge at the end. The average discharge of the Amazon River is about 215,000 to 230,000 cubic meters per second (7,600,000–8,100,000 cubic feet per second, which is the second highest of the top ten rivers in the world. This river shares a 20% supply of water discharge into the ocean. The Amazon River used to flow from the east to the west, but after the upliftment of the Andes Mountain, it was blocking its flow to the Pacific Ocean. Finally, it started to flow from west to east and drained into the Atlantic Ocean.
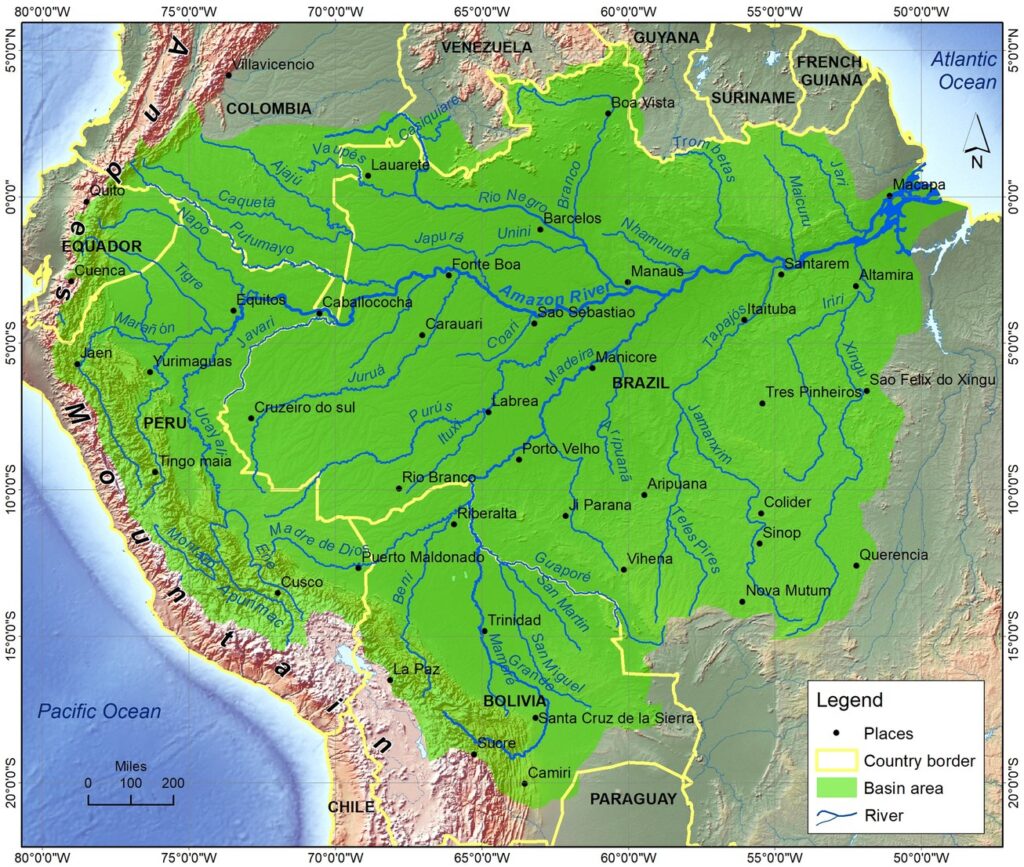
Tributaries of Amazon River
There are more than 1000 tributaries that originated in the Guiana Highlands, the Brazilian Highlands, and the Andes Mountains. The Amazon River Map shows that it has six major tributaries named the Japura, Jurua, Madeira, Negro, Purus, and Xingu Rivers, each of which are more than 1000 miles (1600 kilometers). The Madeira River is the longest tributary more than 2000 miles (3200 kilometers) long. The total length of the Amazon River was calculated as 6,992 km (4,345 mi) by the Brazilian Institute of Space Research (INPF).
Amazon River Basin
Amazon River basin is the largest river basin in the world, which is shown in green color on the Amazon River Map. The Basin area covers approximately 7,050,000 square kilometers (2,720,000 square miles), which is 40% of the total area of South America. This river drains the area of Quito in Peru in the west, to across Brazil and the Atlantic in the east. The Amazon River Map shows that the Amazon River Basin extends from the 5° north latitude to 20° south latitude. Most of the water sources come from the Andean Plateau, just near the east of the Pacific Ocean.
Tributaries of the Amazon River flow through the dense forest areas that are flooded in each rainy season. The river rises higher than 9 meters (30 feet) each year. Thus, large parts of areas of the Amazon River basin are inundated in the rainy season, which covers 350,000 square kilometers (140000 square miles), which is only 110,000 square kilometers (42000 square miles) in the dry season. The water discharge in the rainy season is 300,000 cubic meters per second (11,000,000 cubic feet per second). This river supplies 20% of the earth’s fresh water in the ocean.
