Relocation diffusion is one cultural diffusion that refers to the spread of cultural elements, concepts, or innovations when individuals or groups physically move from one area to another. This diffusion occurs as people migrate, bringing their cultural customs, beliefs, and innovations to new locations, impacting the local culture in the new society of the destination place.
Relocation diffusion is a slow and ongoing process that facilitates the transfer of cultural characteristics from one place to another. This can lead to the creation of new cultures, the merging of current cultures, and the dissemination of fresh ideas and practices.
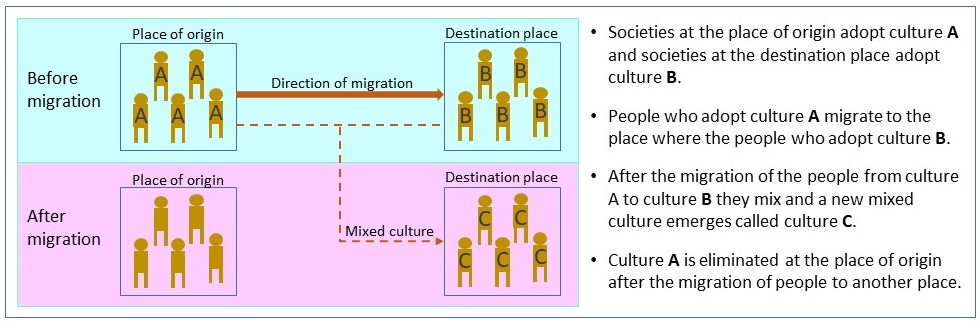
Relocation diffusion occurs through the following processes.
1. Migration of people
Relocation diffusion occurs when individuals migrate from one place to another. When groups of people migrate, they bring their cultural beliefs, traditions, and practices with them to their destination places.
2. Contact with new society
Migrated people adjust to new society at their destination, to establish a new social environment with local society. They exchange ideas, customs, and practices between migrants and local communities.
3. Assimilation of society
When migrated people interact with the new society, they adopt cultural elements from the new societies at their destination. As time passes, this process leads to the fusion of cultures resulting in a new cultural identity.
4. Cultural spreading
Large numbers of migrants from the same initial location will continue to spread their culture, beliefs, and customs throughout the destination’s cultures until their original culture becomes ingrained.
Facts of Relocation Diffusion
1. Relocation diffusion and expansion diffusion
Relocation diffusion is different than expansion diffusion in the context of the spreading cultural traits. One of the important features of relocation diffusion is the loss of cultural traits at the original location when individuals or groups of people migrate and bring their cultural practices to new locations. But expansion diffusion is the cultural traits that still exist in their original place although cultural traits spread outside the place of origin allowing continued growth and expansion in many places.
2. Migration of people from their place of origin
Migration plays a crucial role in relocation diffusion by enabling the transfer of individuals and their cultural attributes to various locations. When migrants establish themselves in unfamiliar areas, they bring their traditions, languages, and practices to the residents. This exchange encourages cultural diversity as different traditions merge, resulting in new cultural environments that showcase the contributions of immigrants and the local populations.
3. Cultural globalization
The enduring impacts of relocation diffusion on society and culture are significant, particularly in the framework of globalization. When individuals move and form communities beyond their borders, they weave together varied social fabrics that showcase diverse influences. This amalgamation can enhance cultural experiences but it may also create conflicts between traditional customs and emerging practices. Gradually, these interactions mold identities, affect social norms, and play a role in the continuous development of cultures in a globalized landscape.
Examples of Relocation Diffusion
1. Buddhism
Buddhism originated in Nepal and India around 500 BC. It spread to most of Central and East Asia through the movement of people along the trade route and migration. Within a few centuries, Buddhism disappeared from its origin but flourished in East and Southeast Asia and remained a dominant religion. Buddism made many changes as it reached peoples of different civilizations. Buddism ideas were shaped differently based on demands for adapting them to local customs.
2. Christianity
Christianity originated in the modern-day Israel and Palestine states and spread worldwide through relocation diffusion. In the beginning, Cristian sprayed their teaching throughout the diverse places of the Roman Empire such as Rome, Alexandria, and Constantinople to establish a Christian society
Christianity started to spread to America, Africa, and Asia through European colonization and missionary activities in the late 15th Century. Christianity changed into various forms based on indigenous beliefs and practices, particularly in Latin America. Thus, forms of Christianity on this continent are significantly different from the Mediterranean.
Christianity is currently a minority religion in the Middle East, where it originated, particularly after the birth of Islam in the seventh century. The faith has spread all over the world influencing nations and civilizations despite its declining numbers in its birthplace.
3. English Language
Germanic languages spoken by groups like the Angles, Saxons, and Jutes who immigrated to Britain in the early Middle Ages are the source of the English language. Latin, French, and other languages were incorporated into it as it developed into Middle and eventually Modern English.
During the 17th through 20th centuries, British colonization and trade led to the export of English to other parts of the world, including North America, Australia, New Zealand, and parts of Africa and Asia.
English has been modified to fit local linguistic contexts in places like the Philippines and India, giving rise to distinctive dialects and pidgins. The language is often taught as a second language in regions like Scandinavia, where the populace speaks it fluently.
Ironically, Old English, the dialect that gave rise to Modern English, is primarily a topic of scholarly research and is hardly understandable to contemporary speakers. The language has become very diverse from its origins as it has changed and adapted to many geographical areas.
4. Curry dish
This dish spread from India to Britain in the 17th century. Curry spread to the Caribbeans, Japan, and Singapore in the 19th century. Curry originated in India and spread to the western hemisphere. It is so popular in the UK that is often called “adopted national dish”.
Curry houses are common in the UK and are related to spicy food with complex preparation and rich ingredients. In India, curry is simply a sauce. Curries are simple meals of vegetables, onions, and salt boiled in water that is called a stew or a broth in Europe.
5. American Log Cabin
Originally popularized in Scandinavia, log cabins are now more frequent in the USA and less common in Scandinavia. An essential component of the American character, the log cabin or log house is linked to the pioneer culture and rugged way of life of the first people to settle in North America (Belonsky, 2018).
The earliest wave of European immigrants to America, particularly from Scandinavia, carried log cabins when they arrived on the northeastern U.S. shore. As modern housing began to supplant log cabins in their original European home, the log cabin began to spread throughout much of the United States and Canada in the 19th century through a twin-layered process of relocation diffusion.
Brick homes quickly replaced log cabins in the 20th century and started to disappear from much of the northeastern United States. However, as migrants moved westward into the American hinterland from the northeastern United States, this architectural style flourished over the American plains.
As a result, the log cabin underwent a two-step relocation process, first, expanding from Scandinavia to the northeastern United States while vanishing from the former, and then expanding from the northeastern United States to the American Midwest and the South before vanishing from the former once more.
